Functional Coverage
Sunday, 13 March 2022 22:37
Semicon Editor 01
 Introduction to Coverage Typically in verification flow, we do code coverage, but doing code coverage shows only if all the lines of the DUT is executed, if all the possible cases of a expression are covered.
Last Updated ( Sunday, 08 May 2022 23:24 )
Read more...
|
Packing And Unpacking
Sunday, 13 March 2022 22:23
Semicon Editor 01
 Packing And Unpacking Packing performs concatenation of scalars, strings, list elements, or struct fields in the order that you specify. Unpacking performs the reverse operation, splitting a single expression into multiple expressions.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 03 May 2022 19:43 )
Read more...
Macros
Sunday, 13 March 2022 21:01
Semicon Editor 01
 Introduction to Macros Macro definitions specify a name or a pattern that is to be replaced by e code text. e is a truly extensible language. It can be extended all the way down to its syntax and lexicon using macros declared by define-as statements.
Last Updated ( Sunday, 08 May 2022 23:22 )
Read more...
Events And Temporal Expressions Part-IV
Saturday, 12 March 2022 17:34
Semicon Editor 01
 ~[ exp..exp ]
True match variable repeat succeeds every time the subexpression succeeds. This expression creates a number of parallel repeat evaluations within the range.
True match repeat also enables specification of behavior over infinite sequences by repeating an infinite number of occurrences of a temporal expression.
Last Updated ( Saturday, 12 March 2022 17:35 )
Read more...
Events And Temporal Expressions Part-III
Saturday, 12 March 2022 17:26
Semicon Editor 01
 Introduction to Temporal Expressions
Temporal expressions provide a declarative way to describe temporal behavior. The e language provides a set of temporal operators and keywords that can be uses to construct temporal expressions.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:02 )
Read more...
Events And Temporal Expressions Part-II
Thursday, 10 March 2022 22:45
Semicon Editor 01
 sys.any This event is a special event that defines the finest granularity of time. The occurrence of any event in the system causes an occurrence of the any event at the same tick. In stand-alone e program operation (that is, with no simulator attached), the sys.any event is the only one that occurs automatically. It typically is used as the clock for stand-alone operation.
Last Updated ( Sunday, 08 May 2022 23:23 )
Read more...
Constraints And Generation Part-III
Thursday, 10 March 2022 21:34
Semicon Editor 01
 Invoking Generation Generation is required before we can do anything meaning full with e language. There are two ways of invoking generation. Generation is invoked automatically when generating the tree of structures starting at sys.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 03 May 2022 19:48 )
Read more...
Events And Temporal Expressions Part-I
Sunday, 06 March 2022 23:04
Semicon Editor 01
 Introduction to Events The e language provides temporal constructs for specifying and verifying behavior over time. All e temporal language features depend on the occurrence of events, which are used to synchronize activity with a simulator and within the e program.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:01 )
Read more...
Constraints And Generation Part-III
Friday, 04 March 2022 16:01
Semicon Editor 01
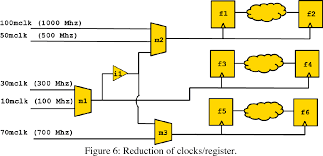 keep soft This suggests default values for fields or variables in the struct or its subtree, or describes suggested relationships between field values and other items in the struct or its subtree. The following restrictions apply.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:04 )
Read more...
Constraints And Generation Part-II
Friday, 04 March 2022 16:00
Semicon Editor 01
 Defining Constraints This section describes in detail with examples on how to define constrains. This is basically more theory of what we have seen in last section.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:03 )
Read more...
Constraints And Generation part 1
Friday, 04 March 2022 14:33
Semicon Editor 01
 Generation And Constraints Test generation is a process producing data layouts according to a given specification. The specifications are provided in the form of type declarations and constraints. Constraints are statements that restrict values assigned to data items by test generation.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:05 )
Read more...
Interfacing With Simulators Part-II
Tuesday, 01 March 2022 15:53
Semicon Editor 01
 Simulation-related constructs | This section covers the simulation related constructs that can be used withing e language, some of them are as given below. | 'HDL pathname'
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 03 May 2022 19:47 )
Read more...
Interfacing With Simulators Part-I
Tuesday, 01 March 2022 15:00
Semicon Editor 01
 Interfacing with simulator
In Verilog linking any foreign language is through PLI, and in VHDL is FLI. Since e language is a foreign language, it has to go though PLI of Verilog and FLI of VHDL.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 29 March 2022 00:05 )
Read more...
Conditional Flow Control Part-III
Sunday, 27 February 2022 16:00
Semicon Editor 01
 File Iterative Control
In e the way we open and read ASCII files is slightly different then C and C++. There are two types of looping constructs that are provided to help with handling ASCII files. for each line in file
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 24 May 2022 23:29 )
Read more...
Conditional Flow Control Part-II
Sunday, 27 February 2022 15:52
Semicon Editor 01
 Iterative Control There are four types of iterative actions in e: While
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 24 May 2022 23:22 )
Read more...
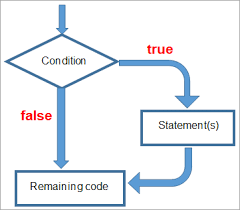
Conditional Flow Control Part-I
Sunday, 27 February 2022 15:33
Semicon Editor 01
 Conditional Flow Control: Conditional flow like in any other programming language is used for controlling execution a block of code, when a condition is true. if then else if then else is used for checking for a condition and if condition is true, then the block of code inside the {} is excuted.
Last Updated ( Tuesday, 24 May 2022 23:09 )
Read more...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 3 of 118 |


